A porous trimetallic Au@Pd@Ru nanoparticle system: synthesis, characterisation and efficient dye degradation and removal - Journal of Materials Chemistry A (RSC Publishing)

Hollow Palladium Nanoparticles Facilitated Biodegradation of an Azo Dye by Electrically Active Biofilms

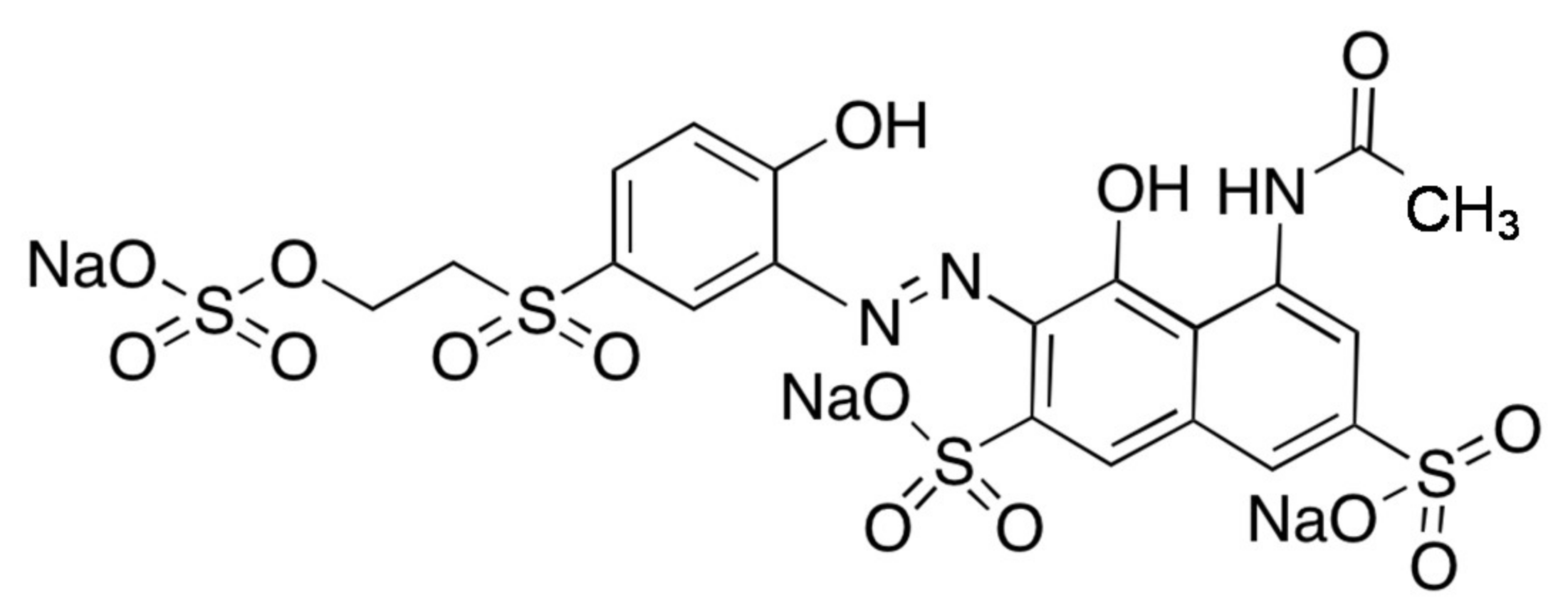
Aluminum based metallic glass powder for efficient degradation of AZO dye and other toxic organic chemicals - US 10,363,548 B2 - PatentSwarm
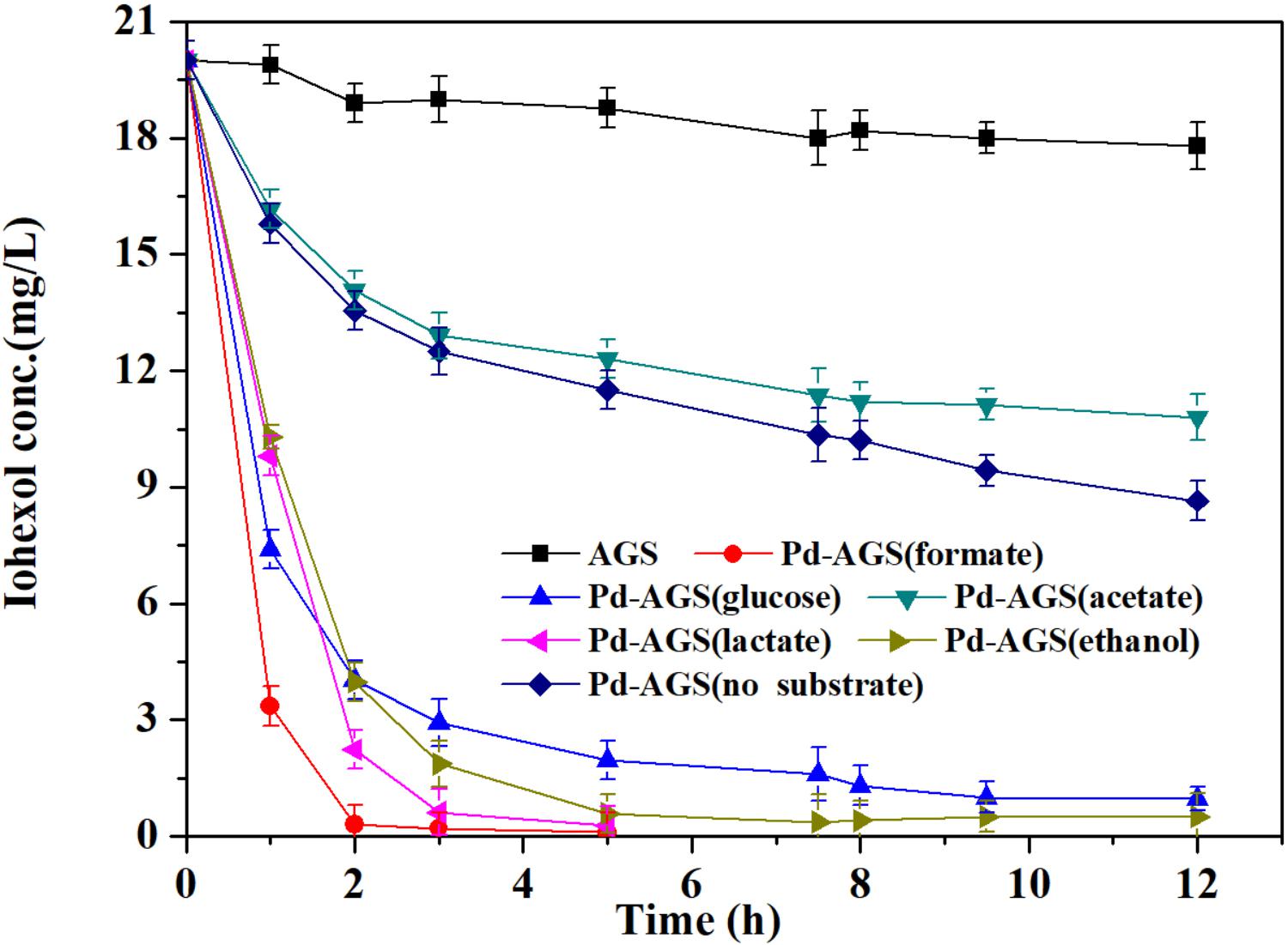
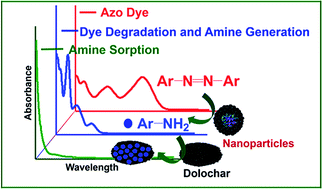
Frontiers | Iohexol Degradation by Biogenic Palladium Nanoparticles Hosted in Anaerobic Granular Sludge | Microbiology
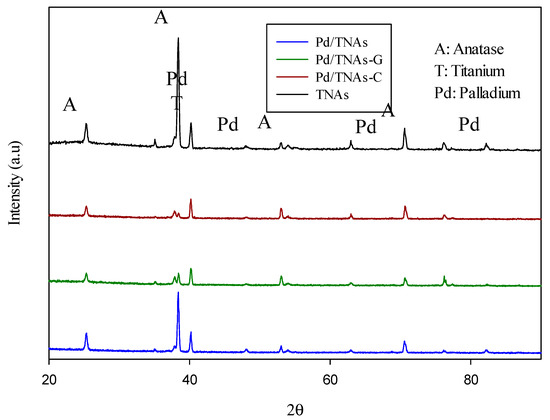
Catalysts | Free Full-Text | Green Synthesized Palladium Coated Titanium Nanotube Arrays for Simultaneous Azo-Dye Degradation and Hydrogen Production | HTML

The time-dependent UV-vis absorption spectra of azo dyes degraded by... | Download Scientific Diagram
PDF) Hollow Palladium Nanoparticles Facilitated Biodegradation of an Azo Dye by Electrically Active Biofilms

Remediation of azo-dyes based toxicity by agro-waste cotton boll peels mediated palladium nanoparticles - ScienceDirect

Remediation of azo-dyes based toxicity by agro-waste cotton boll peels mediated palladium nanoparticles - ScienceDirect

Remediation of azo-dyes based toxicity by agro-waste cotton boll peels mediated palladium nanoparticles - ScienceDirect

Highly efficient degradation of azo dyes by palladium/hydroxyapatite/Fe3O4 nanocatalyst. | Semantic Scholar

Degradation of methylene blue and methyl orange by palladium-doped TiO2 photocatalysis for water reuse: Efficiency and degradation pathways - J. Clean. Prod. - X-MOL
Catalysts | Free Full-Text | Photocatalytic Degradation of Azo Dye Reactive Violet 5 on Fe-Doped Titania Catalysts under Visible Light Irradiation | HTML

Highly efficient degradation of azo dyes by palladium/hydroxyapatite/Fe3O4 nanocatalyst. | Semantic Scholar

Highly efficient degradation of azo dyes by palladium/hydroxyapatite/Fe3O4 nanocatalyst - ScienceDirect

Polyaniline Supported Palladium Catalyzed Reductive Degradation of Dyes Under Mild Condition | Bentham Science

Highly efficient degradation of azo dyes by palladium/hydroxyapatite/Fe3O4 nanocatalyst. | Semantic Scholar

Remediation of azo-dyes based toxicity by agro-waste cotton boll peels mediated palladium nanoparticles - ScienceDirect

Hollow Palladium Nanoparticles Facilitated Biodegradation of an Azo Dye by Electrically Active Biofilms

Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles with carboxymethyl cellulose for degradation of azo-dyes - ScienceDirect

![PDF] Decolourization of azo dyes using magnesium-palladium system. | Semantic Scholar PDF] Decolourization of azo dyes using magnesium-palladium system. | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/7ed96efa0c0b60bb92f796ce9f47fe4ef2369135/12-Table4-1.png)


![PDF] Decolourization of azo dyes using magnesium-palladium system. | Semantic Scholar PDF] Decolourization of azo dyes using magnesium-palladium system. | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/7ed96efa0c0b60bb92f796ce9f47fe4ef2369135/5-Figure4-1.png)